XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS: Comprehensive Guide and Benefits
Introduction to XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS
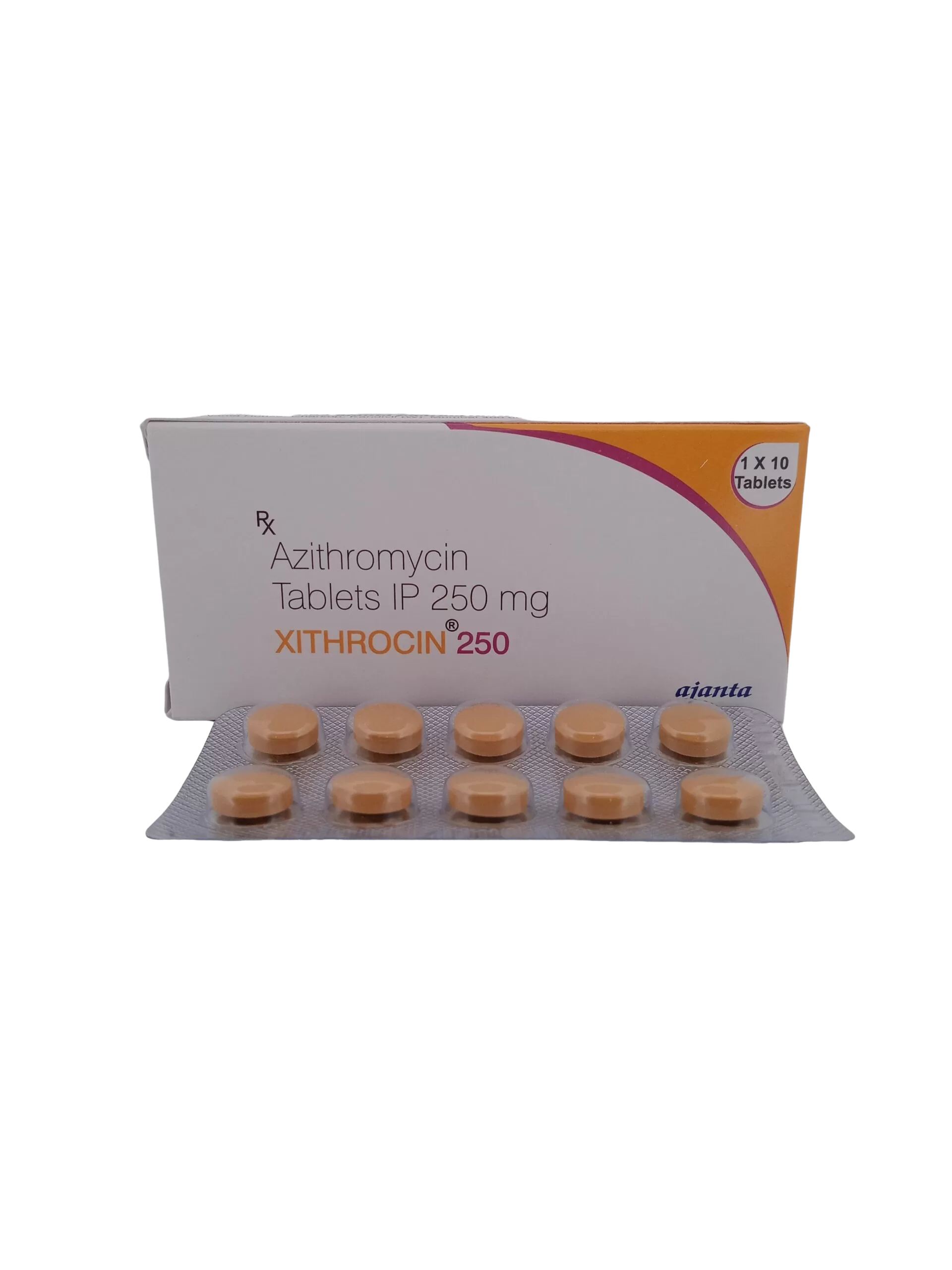
Xithrocin 250 mg: Azithromycin for Effective Bacterial Infection Treatment
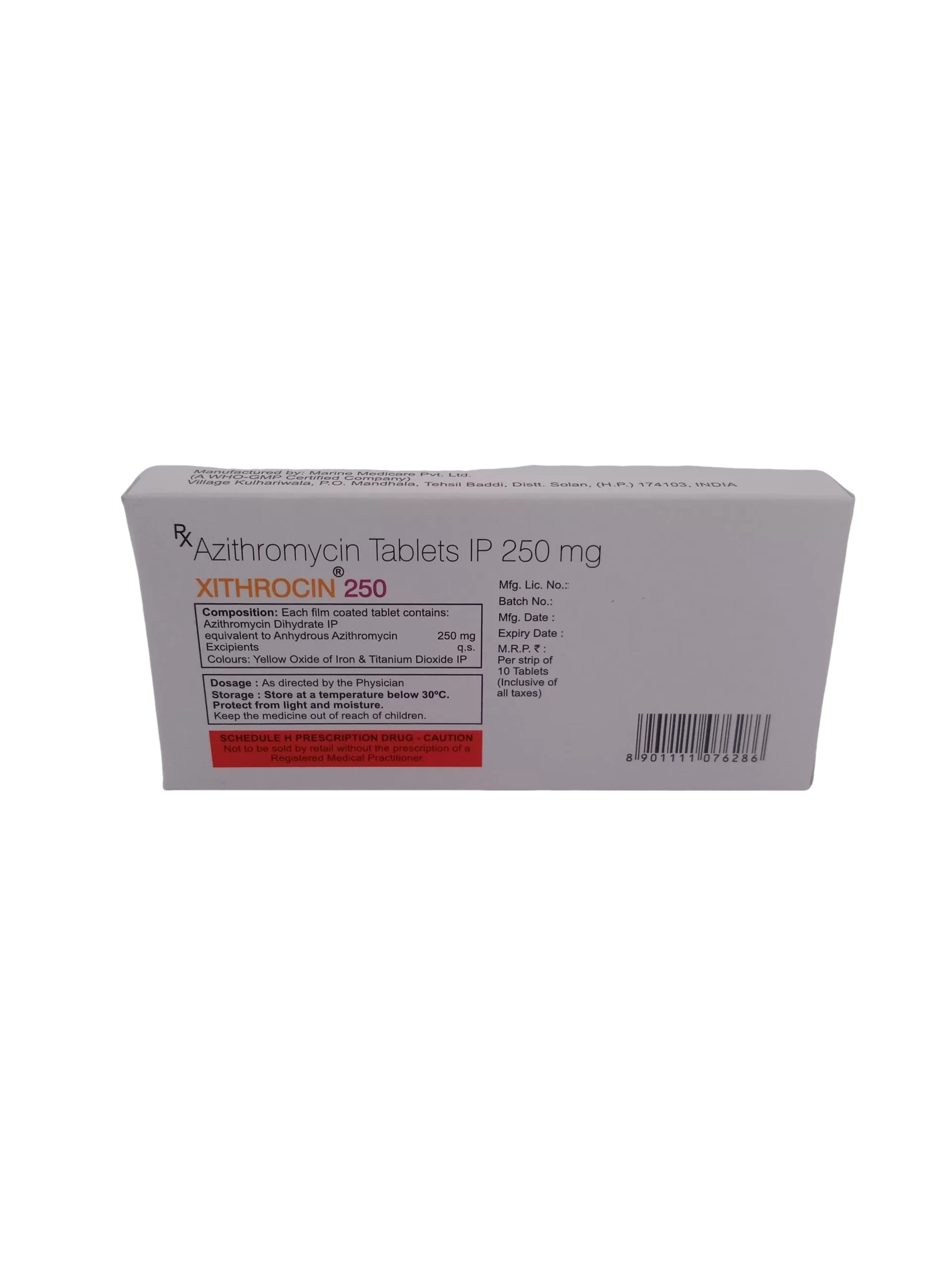
Xithrocin 250 mg, containing azithromycin, is a powerful broad-spectrum antibiotic used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory infections, skin infections, and ear infections, among others. Thanks to its fast-acting formula, Xithrocin helps quickly eliminate harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of complications from untreated infections.. This product is carefully formulated to provide effective results while ensuring safety and ease of use.
Key Benefits of XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS
Effective Action – Works efficiently to deliver intended results.
High-Quality Ingredients – Formulated with trusted components for maximum effectiveness.
Safe Usage – Designed for optimal use with minimal side effects.
How XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS Works
The active ingredients in XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS work by targeting key mechanisms in the body to provide the desired benefits. It is widely recommended for its efficacy and safety.
Usage Instructions for XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS
Dosage – Follow the prescribed dosage or as directed by a healthcare professional.
Administration – Best taken at the recommended time to maximize effectiveness.
Precautions – Avoid exceeding the recommended dose and consult a doctor if necessary.
Medicinal Advantages of XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS
Reliable Results – Proven to deliver desired outcomes.
Supports Health – Helps improve well-being with consistent use.
Minimal Side Effects – Designed to reduce adverse reactions.
Off-Label Uses of XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS
While primarily used for its main purpose, some users have reported additional benefits in related health areas. Consult a healthcare provider for more information.
Expert Advice for Optimal Use
Consultation – Always check with a doctor before use, especially if you have existing health conditions.
Safe Storage – Keep in a cool, dry place away from children.
Avoid Misuse – Use only as directed to prevent complications.
Storage Instructions
Temperature – Store at room temperature, away from heat and moisture.
Safety Precautions – Keep out of reach of children and pets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How soon does XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS take effect?
A: The effects vary but are generally noticeable within a reasonable timeframe.
Q: Can I use XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS daily?
A: Usage frequency should be based on professional medical advice.
Q: Is XITHROCIN 250 MG – 10 TABLETS safe for pregnant or breastfeeding women?
A: Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended before use.
Q: Are there any side effects?
A: Most users experience minimal or no side effects when taken as directed.